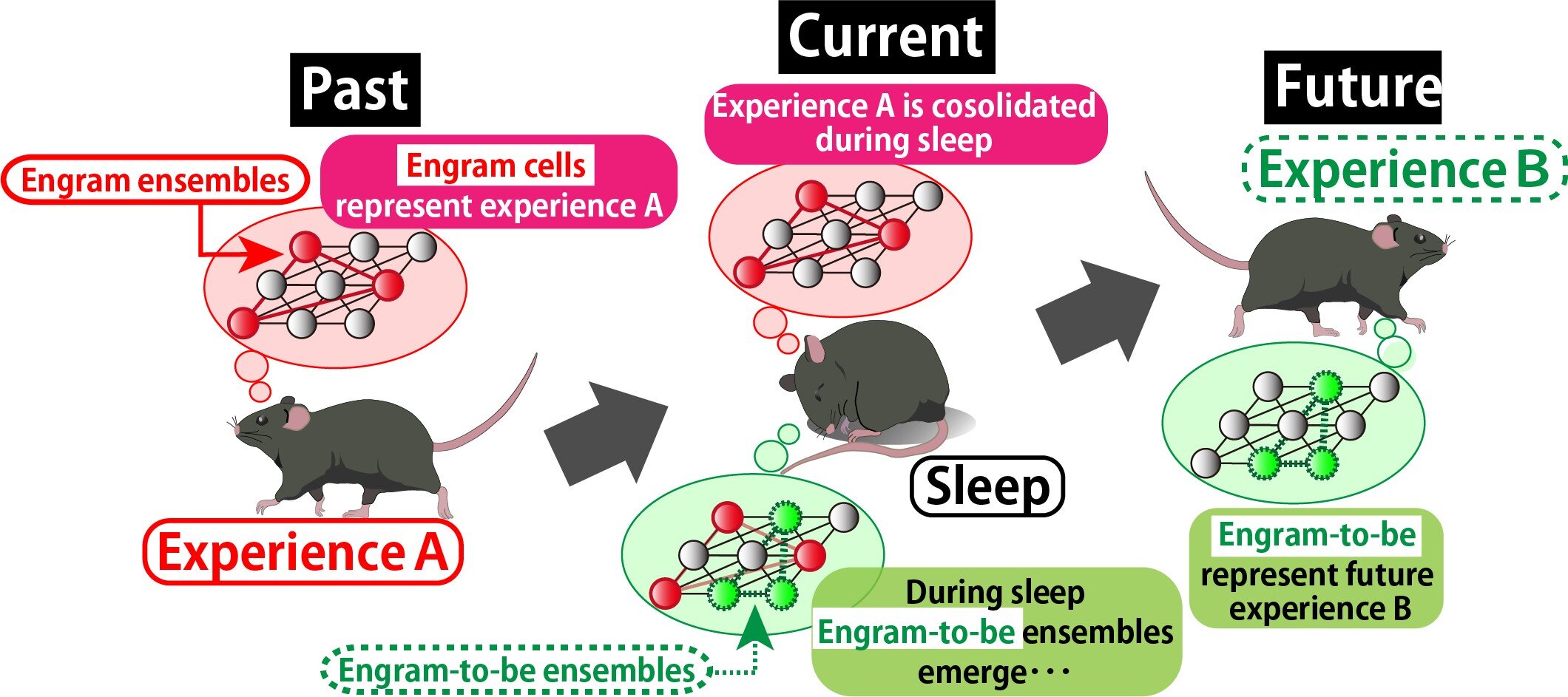
Reminiscence formation, storage, and retrieval are elementary processes that outline who we’re and the way we work together with the world. On the mobile stage, these processes depend on specialised neurons referred to as engram cells—neuronal populations that bodily encode our experiences and permit us to recall them later. Over the previous few many years, scientists have made vital progress in figuring out these neuronal ensembles and understanding some facets of reminiscence allocation.
Though sleep is extensively recognized to be important for reminiscence processing and consolidation, lots of its underlying mechanisms and capabilities are unclear. Conventional views have largely targeted on sleep as a backward-looking course of that serves to strengthen previous experiences, however might it concurrently assist put together the mind for brand spanking new studying?
In a latest effort to deal with this query, a analysis group from Japan, led by Distinguished Professor Kaoru Inokuchi from the College of Toyama, uncovered a twin position for sleep in reminiscence processing. Their paper, which might be printed in Nature Communications on April 28, 2025, explores how the mind concurrently preserves previous recollections whereas getting ready for future ones throughout sleep durations.
The research was co-authored by Specifically Appointed Assistant Professor Khaled Ghandour, additionally from the College of Toyama; Dr. Tatsuya Haga from the Nationwide Institute of Data and Communications Expertise; Dr. Noriaki Ohkawa from Dokkyo Medical College; and Professor Tomoki Fukai from OIST.
The researchers employed a complicated imaging system that mixes stay calcium imaging with engram cell labeling, permitting them to trace neuronal exercise in mice earlier than, throughout, and after studying experiences. This method gave them unprecedented insights into how particular populations of neurons behave throughout totally different cognitive states, together with throughout sleep durations earlier than and after studying occasions.
Their findings revealed that two parallel processes happen throughout post-learning sleep. First, engram cells that encoded an preliminary studying expertise confirmed reactivation patterns—confirming the well-established consolidation course of. Remarkably, additionally they recognized a separate inhabitants of neurons, which they termed “engram-to-be cells,” that turned more and more synchronized throughout post-learning sleep. These cells had been later proven to encode a brand new, totally different studying expertise.
“Engram-to-be cells exhibited elevated coactivity with present engram cells throughout sleep, suggesting that this interplay helps form new reminiscence networks,” explains Prof. Inokuchi.
To know the mechanisms behind this phenomenon, the group developed a neural community mannequin simulating hippocampal exercise. The mannequin steered that synaptic melancholy and scaling, that are mechanisms that modify connection strengths between neurons throughout sleep, are important for the emergence of engram-to-be cells. When these processes had been disabled within the mannequin, the preparation of neurons for future studying was considerably impaired.
The research additionally revealed fascinating dynamics between present engram cells and engram-to-be cells, exhibiting elevated co-activation throughout post-learning sleep. This hints at some type of data switch or coordination between neural networks representing previous and future recollections.
These findings have vital implications for our understanding of studying and reminiscence. They counsel that the standard of sleep between studying periods could decide not solely how effectively we bear in mind what we have already realized, but in addition how successfully we are able to be taught new data. This might affect approaches to schooling, cognitive enhancement, and the remedy of reminiscence problems.
Moreover, the analysis opens new avenues for exploring how sleep disturbances would possibly influence not simply reminiscence consolidation but in addition the mind’s preparedness for future studying challenges. “We imagine that manipulating mind exercise throughout sleep or sleep patterns could uncover strategies to boost reminiscence by unlocking the mind’s latent potential,” says Prof. Inokuchi.
General, this research underscores the crucial position of sleep in sustaining cognitive operate and general well-being. “We would like folks to grasp that sleep is not only about relaxation—it performs a vital position in how the mind processes data,” Prof. Inokuchi concludes, “With that in thoughts, we hope everybody will start to worth sleep extra and use it as a means to enhance their general high quality of life.”
Extra data:
Parallel processing of previous and future recollections by way of reactivation and synaptic plasticity mechanisms throughout sleep, Nature Communications (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-58860-w
Supplied by
College of Toyama
Quotation:
Sleep’s twin position: The way it consolidates recollections whereas getting ready the mind for brand spanking new studying (2025, April 28)
retrieved 28 April 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-04-dual-role-memories-brain.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.