Breast most cancers is changing into more and more treatable, however in some instances the illness can resurface even a long time after a affected person has been declared most cancers free. That is due to cells that detach from the unique tumor and conceal in a dormant state within the breast or different organs.
Little is thought concerning the mechanisms accountable for dormancy in most cancers cells, and even much less is thought about what causes these cells to all of the sudden get up. A brand new research from the laboratory of Israel Prize laureate Prof. Yosef Yarden on the Weizmann Institute of Science, revealed in Science Signaling, reveals the mechanism that places breast most cancers cells to sleep, in addition to the rationale that they emerge from dormancy extra aggressive than they had been earlier than they grew to become dormant.
From the earliest stage of embryonic growth, by way of sexual maturation to the manufacturing of breast milk throughout being pregnant and after childbirth, breast tissue adjustments all through a girl’s life. These adjustments are made attainable by the metamorphosis that breast tissue cells endure, from the early developmental stage, often known as mesenchymal, when the cells are spherical, extremely cellular and dividing quickly, to the extra mature, epithelial stage, when they’re considerably cubical, much less lively and dividing slowly.
The cells transfer forwards and backwards between these levels in a managed and gradual course of, however typically they go uncontrolled, dividing quickly and changing into malignant. This most cancers course of begins when mature cells return to their earlier, developmental stage, which permits them to divide quickly, create tumor tissue and even migrate to different tissues. In a while, nonetheless, the most cancers can profit from precisely the alternative course of: Cells which have unfold all through the physique can revert to their mature state, changing into motionless and sluggish. Primarily, they grow to be dormant.
Due to the key similarities between entry into dormancy and the maturation means of epithelial cells, scientists in Yarden’s lab in Weizmann’s Immunology and Regenerative Biology Division postulated that they may be capable to induce a state of dormancy in breast most cancers cells by imitating the pure course of.
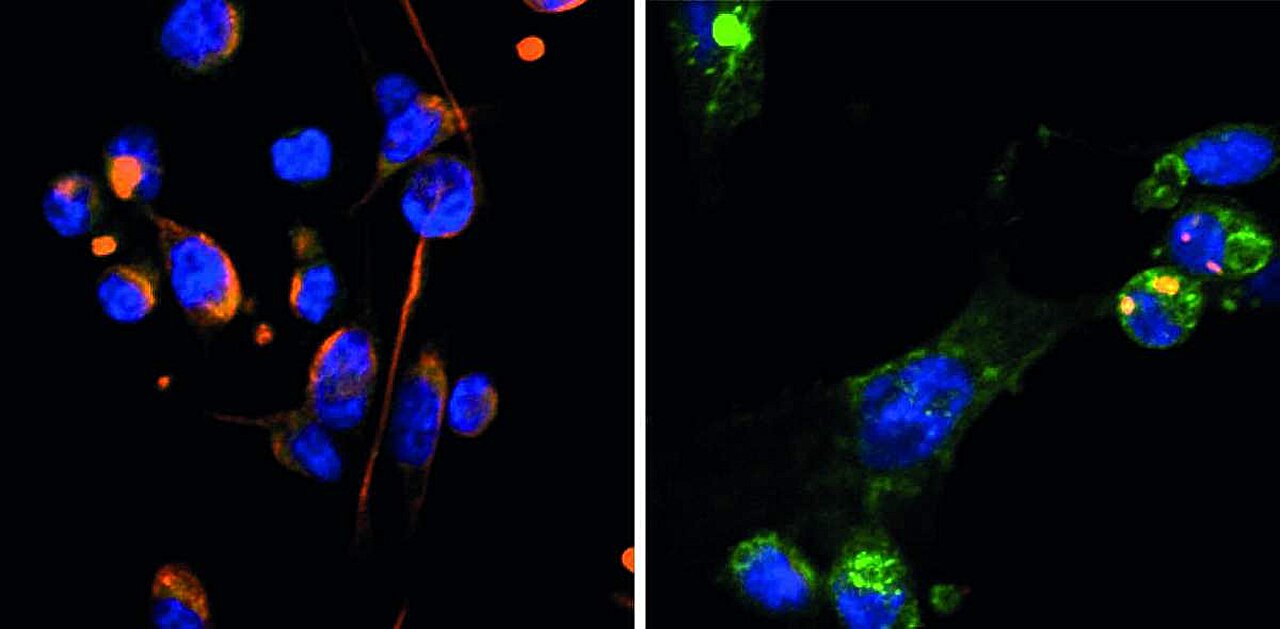
Utilizing a three-dimensional mannequin of a cancerous tumor surroundings developed by Dr. Dalit Barkan of Haifa College, the researchers, led by Dr. Diana Drago-Garcia from Yarden’s workforce, genetically modified human breast most cancers cells of essentially the most aggressive kind, referred to as triple-negative breast most cancers, to provide larger ranges of OVOL proteins, that are identified to be concerned within the pure maturation of epithelial cells.
The mannequin confirmed that growing the expression of two OVOL proteins halts the lifecycle of aggressive most cancers cells and induces dormancy. In parallel, the researchers confirmed, in feminine mice implanted with human tumor tissue, that over-expression of OVOL inhibits the expansion of the most cancers.
Though halting the lifecycle of most cancers cells and slowing tumor development may sound like excellent news and even perhaps the idea for a future therapy, it’s identified that most cancers sufferers’ breast tissue accommodates elevated ranges of one of many OVOL proteins.
The scientists subsequently hypothesized that whereas this protein, OVOL1, slows most cancers within the quick time period, it’s helpful to cancerous cells in the long run, enabling them to enter a state of dormancy and survive for years with out being detected. When circumstances within the physique change and the extent of OVOL1 drops, the most cancers comes again to life and is extra aggressive than ever earlier than.
Armed with these findings, the researchers started to review how the most cancers impacts the expression ranges of OVOL proteins, placing tumor cells to sleep or waking them up. One key discovering was that sure development elements increase OVOL1 expression, however the steroid hormone estrogen suppresses it. The scientists went on to point out that sufferers with low ranges of estrogen receptors and excessive ranges of OVOL1 are likely to develop extra aggressive most cancers and have decrease possibilities of survival.
“These findings might pave the way in which for stopping most cancers cells from going dormant or stopping dormant cells from reawakening,” Yarden says. “We all know, for instance, that fats tissue takes management of estrogen manufacturing throughout menopause. So, we are able to assume that weight achieve in older ladies who had most cancers once they had been youthful might improve the chance of dormant most cancers resurfacing due to elevated estrogen manufacturing and the related drop in OVOL1 expression. Sooner or later, these hypotheses might be examined in animal fashions and in human sufferers.”
Altering of their sleep
One of many questions that remained unanswered was why breast most cancers tends to be extra aggressive when it awakens from a state of dormancy. To uncover the underlying mechanisms, the researchers traced the molecular signaling pathway by way of which OVOL1 induces dormancy. They found that this pathway triggers an accumulation of unstable molecules often known as free radicals, which ends up in widespread mobile harm, cell cycle arrest and dormancy. This buildup was shocking, since these molecules had not beforehand been linked to dormancy in most cancers cells.
Later, the researchers, working with Prof. Emeritus Yosef Shiloh of Tel Aviv College, confirmed that the continual mobile stress throughout the dormant cells, ensuing from the buildup of the free radicals, adjustments the expression and performance of proteins within the cells’ nuclei, which home their genetic materials. Consequently, the genetic materials is oxidized and its integrity is compromised, as is the functioning of three key proteins concerned in DNA restore mechanisms.
The scientists consider that the widespread harm to the genetic materials and the failure of the restore mechanisms clarify why, when a most cancers cell awakens, it carries quite a few mutations, making it extra aggressive and immune to therapy.
“The frequent perception is that dormant most cancers cells exist in a suspended state, however we’ve proven that in their so-called sleep they accumulate DNA mutations due to the oxidative course of, and so they endure a serious change,” Yarden explains.
“This discovery is in line with the evaluation of tissue samples from aggressive breast most cancers tumors. Importantly, breast most cancers is just not the one malignancy that enters a state of dormancy, so understanding the mechanisms of dormancy might result in new remedies for varied different forms of most cancers, as properly.”
Extra data:
Diana Drago-Garcia et al, Re-epithelialization of most cancers cells will increase autophagy and DNA harm: Implications for breast most cancers dormancy and relapse, Science Signaling (2025). DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.ado3473
Quotation:
How breast most cancers cells grow to be dormant and stay undetected for years, and why they later get up and metastasize (2025, April 22)
retrieved 22 April 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-04-breast-cancer-cells-dormant-undetected.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.