A newly revealed research within the Journal of Medical Entomology gives essential insights into the emergence of babesiosis within the Mid-Atlantic area, documenting human instances and the presence of Babesia microti in native tick populations.
The article, titled “Rising Babesiosis within the Mid-Atlantic: Autochthonous Human Babesiosis Instances and Babesia microti (Piroplasmida: Babesiidae) in Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae) and Ixodes keiransi (Acari: Ixodidae) Ticks from Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia, 2009-2024,” presents a complete evaluation of the rising public well being risk posed by this tick-borne illness.
The research confirms that babesiosis, traditionally concentrated within the Northeast and Higher Midwest, is now increasing within the Mid-Atlantic area. The analysis highlights an rising variety of regionally acquired (autochthonous) human instances and the detection of Babesia microti, the first causative agent of human babesiosis, in blacklegged ticks (Ixodes scapularis) and Ixodes keiransi ticks.
The research was carried out by Ellen Stromdahl, Ph.D., retired entomologist on the Vector-Borne Illness Laboratory, Protection Facilities for Public Well being-Aberdeen, together with 21 colleagues from the Maryland Division of Well being, Delaware Division of Pure Assets and Environmental Management, Outdated Dominion College, Delaware Technical Group School, Virginia Division of Well being, College of Richmond, DC Well being, U.S. Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention, U.S. Meals & Drug Administration, West Virginia Division of Well being, and Mayo Clinic.
Key findings embody:
- Autochthonous human babesiosis instances have been reported for the primary time from the Mid-Atlantic U.S. jurisdictions of Maryland, Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia between 2009 and 2024.
- Babesia microti was detected in ticks collected from Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, West Virginia, and DC.
- The research gives the primary report of Ixodes keiransi as a possible vector of Babesia microti.
- The info recommend that babesiosis is changing into a rising concern in areas the place it was beforehand thought-about uncommon or absent.
“The findings underscore the necessity for elevated surveillance, public consciousness, and preventive measures towards tick-borne ailments within the Mid-Atlantic area,” says Stromdahl. “Well being care suppliers ought to take into account babesiosis within the differential analysis for sufferers with febrile sickness, notably throughout peak tick-activity seasons.”
Babesiosis, brought on by microscopic parasites that infect purple blood cells, can vary from asymptomatic to extreme sickness, notably in immunocompromised people. Babesiosis might be extreme within the aged or immunocompromised, particularly when sufferers have concurrent infections with Borrelia burgdorferi (the micro organism that causes Lyme illness).
Prognosis might be troublesome, because the illness is uncommon, and early signs of babesiosis resemble circumstances extra prone to be anticipated in aged populations or related to different extra widespread tick-borne ailments. In consequence, babesiosis is perhaps misdiagnosed or handled empirically with antibiotics sometimes prescribed for Lyme illness or anaplasmosis, akin to doxycycline. Nonetheless, antibiotics alone should not efficient towards babesiosis, making early and correct analysis essential.
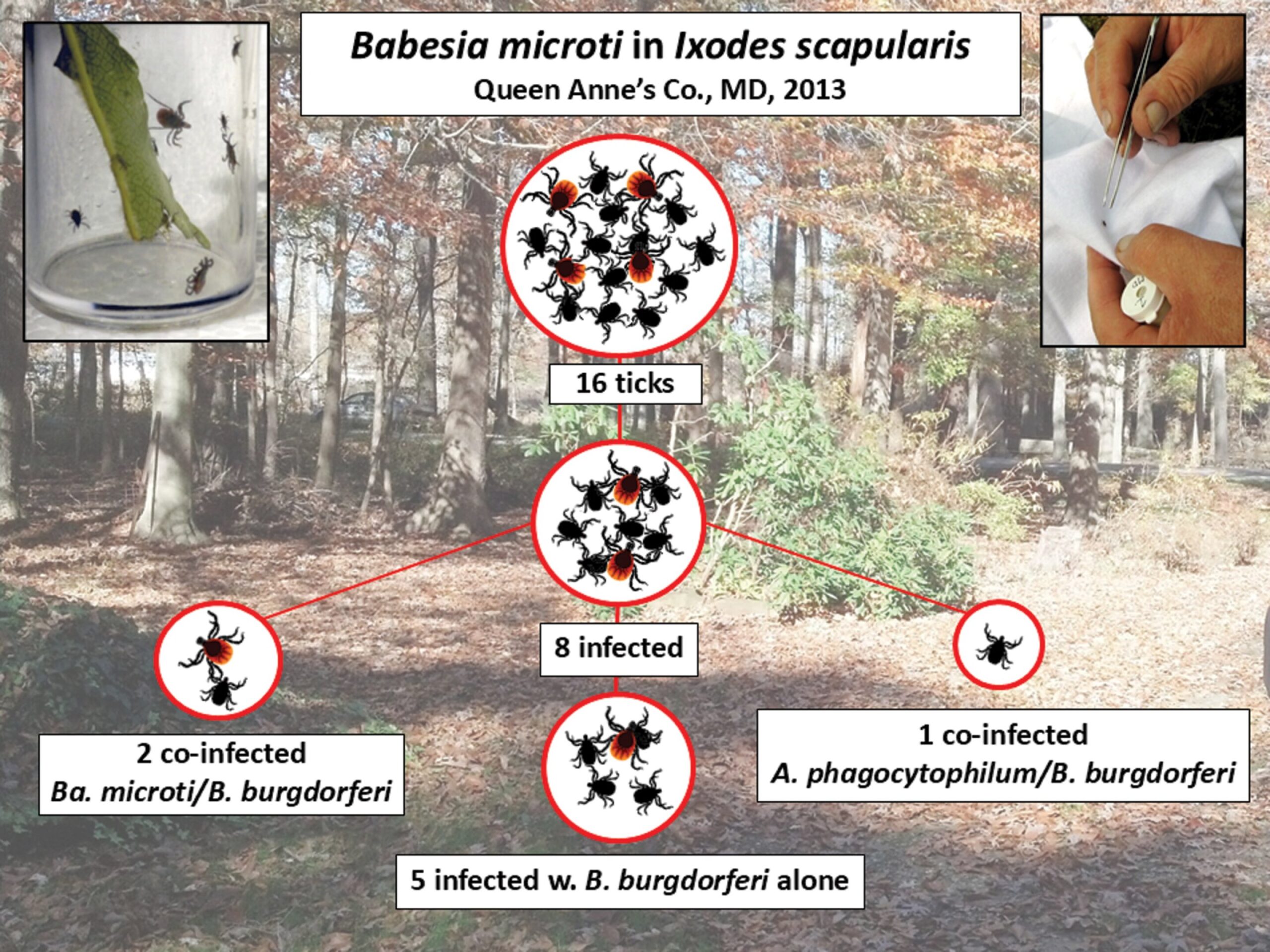
Moreover, coinfection of Ixodes scapularis with B. microti and B. burgdorferi is widespread. On this research, half of the ticks optimistic for B. microti have been additionally contaminated with B. burgdorferi, and one was triple-infected with Anaplasma phagocytophilum, B. burgdorferi, and B. microti. Additional, extra I. scapularis from Maryland and Virginia have been discovered concurrently contaminated with A. phagocytophilum, B. burgdorferi, B. microti, and Borrelia miyamotoi. Practitioners have to be alert to concurrent infections that may complicate analysis and remedy.
This analysis emphasizes the significance of enhanced public well being surveillance, together with conducting thorough investigations of all potential human instances of babesiosis and conducting tick surveillance at any time when attainable.
Training about this rising danger, together with methods to stop an infection within the first place, methods to acknowledge an infection, and applicable remedy, must be elevated for medical suppliers, public well being practitioners and the overall inhabitants.
Extra data:
Ellen Y Stromdahl et al, Rising babesiosis within the mid-Atlantic: autochthonous human babesiosis instances and Babesia microti (Piroplasmida: Babesiidae) in Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae) and Ixodes keiransi (Acari: Ixodidae) ticks from Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia, 2009 to 2024, Journal of Medical Entomology (2025). DOI: 10.1093/jme/tjaf054
Quotation:
Research reveals rising instances of babesiosis in Mid-Atlantic area (2025, April 29)
retrieved 29 April 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-04-reveals-emerging-cases-babesiosis-mid.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.