Coronary heart
Affected person brochure
Discover info for sufferers and households to know and navigate organ donation and transplantation under:
Questions and solutions for transplant candidates about:
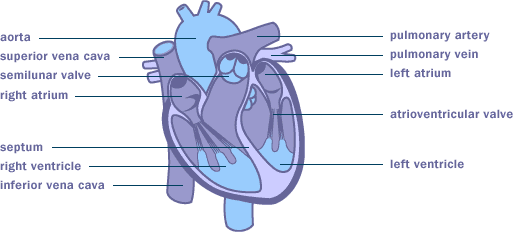
The guts
Capabilities of the center
The guts is a robust, muscular, cone-shaped organ. It’s situated behind the breastbone between the lungs. It pumps blood all through the physique.
Blood that not carries oxygen flows from the center to the lungs, the place it provides up wastes and will get new oxygen. From there, the blood returns to the center and is pumped to the remainder of the physique.
Coronary heart failure occurs when the center can not pump sufficient blood to satisfy the physique’s wants. Start defects, or any situation that damages or overloads the center muscle, could cause it. Therapy is determined by the reason for coronary heart failure and the age and situation of the affected person.
Coronary heart transplant procedures
Most coronary heart transplants contain changing the affected person’s coronary heart with the center from a deceased donor. In uncommon circumstances, the affected person’s native coronary heart is just not eliminated; this is called a heterotopic transplant.
There even have been a couple of transplants involving a dwelling coronary heart donor. This may occasionally happen if one affected person receives a heart-lung mixture transplant however their coronary heart is in good situation. This affected person’s coronary heart could then be transplanted into one other recipient. This is called a “domino” coronary heart transplant.
Causes for coronary heart transplant
| Coronary heart analysis classes | Coronary heart diagnoses |
|---|---|
| Cardiomyopathy |
Dilated Myopathy: Idiopathic Dilated Myopathy: Myocarditis Dilated Myopathy: Different Specify Dilated Myopathy: Submit Partum Dilated Myopathy: Familial Dilated Myopathy: Adriamycin Dilated Myopathy: Viral Dilated Myopathy: Alcoholic Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Restrictive Myopathy: Idiopathic Restrictive Myopathy: Amyloidosis Restrictive Myopathy: Sarcoidosis Restrictive Myopathy: Endocardial Fibrosis Restrictive Myopathy: Different Specify Restrictive Myopathy: Secondary to Radiation/Chemotherapy |
| Coronary Artery Illness |
Coronary Artery Illness Dilated Myopathy: Ischemic |
| Congenital Coronary heart Illness |
Congenital Coronary heart Illness |
| Valvular Coronary heart Illness |
Valvular Coronary heart Illness |
| Retransplant/Graft Failure |
Coronary heart Retransplant/Graft Failure: Coronary Artery Illness Coronary heart Retransplant/Graft Failure: Different Specify Coronary heart Retransplant/Graft Failure: Non-Particular Coronary heart Retransplant/Graft Failure: Acute Rejection Coronary heart Retransplant/Graft Failure: Hyperacute Rejection Coronary heart Retransplant/Graft Failure: Major Failure Coronary heart Retransplant/Graft Failure: Persistent Rejection Coronary heart Retransplant/Graft Failure: Restrictive/Constrictive |
| Different |
Cardiac Illness: Different Specify Coronary heart: Different Specify Most cancers |