Cybersecurity researchers have detailed a now-patched vulnerability in Google Cloud Platform (GCP) that would have enabled an attacker to raise their privileges within the Cloud Composer workflow orchestration service that is based mostly on Apache Airflow.
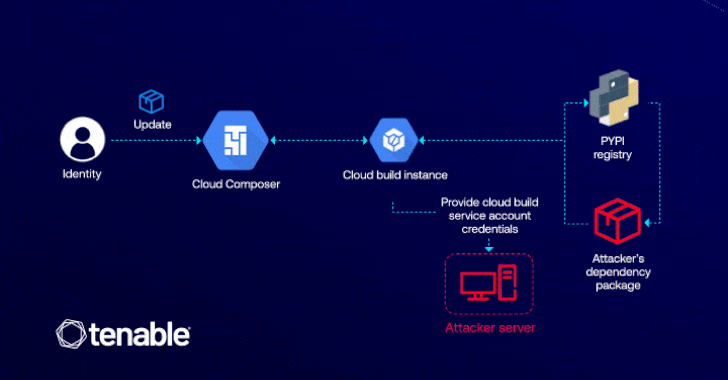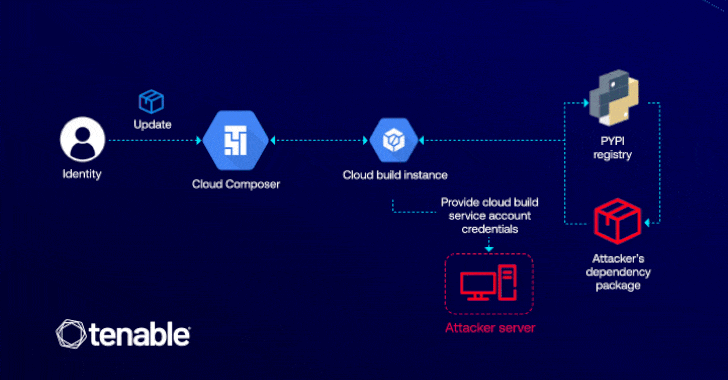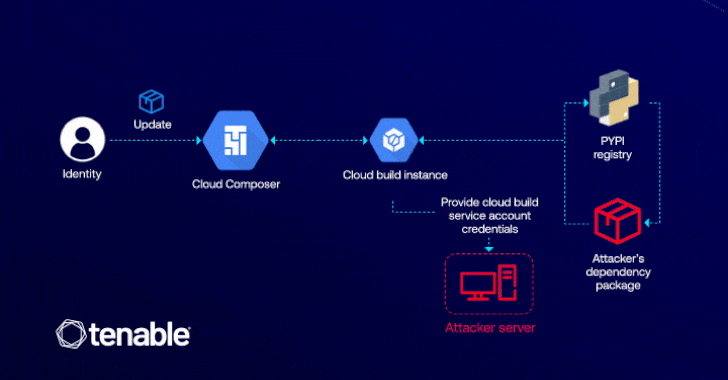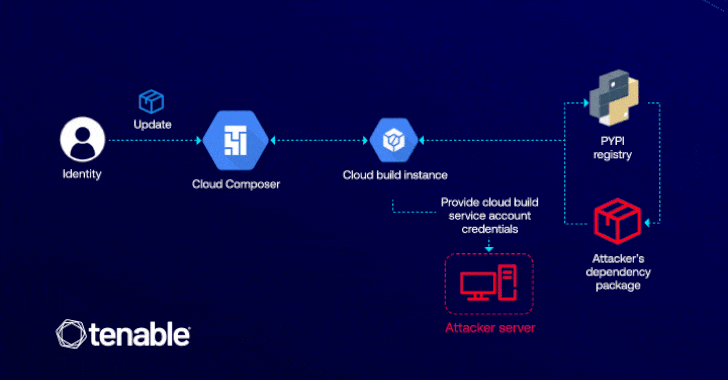
“This vulnerability lets attackers with edit permissions in Cloud Composer to escalate their entry to the default Cloud Construct service account, which has high-level permissions throughout GCP companies like Cloud Construct itself, Cloud Storage, and Artifact Registry,” Liv Matan, senior safety researcher at Tenable, stated in a report shared with The Hacker Information.
The shortcoming has been codenamed ConfusedComposer by the cybersecurity firm, describing it as a variant of ConfusedFunction, a privilege escalation vulnerability impacting GCP’s Cloud Capabilities service that an attacker may exploit to entry different companies and delicate information in an unauthorized method.
The disclosure comes weeks after Tenable detailed one other privilege escalation vulnerability in GCP Cloud Run dubbed ImageRunner that would have allowed a malicious actor to entry container photographs and even inject malicious code — creating cascading results.
Like ImageRunner, ConfusedComposer is one other instance of the Jenga idea, which causes safety points to be inherited from one service to the opposite when cloud service suppliers construct new companies atop current ones.
The exploit hinges on the attacker having permission to edit a Cloud Composer atmosphere (i.e., composer.environments.replace), which could possibly be exploited to inject a malicious Python Bundle Index (PyPI) package deal that is able to escalating privileges via Cloud Construct.
The assault is made attainable as a consequence of the truth that Cloud Composer permits customers to put in customized PyPI packages of their environments, thereby enabling an adversary to execute arbitrary code throughout the related Cloud Construct occasion through the use of set up scripts inside their malicious package deal.
“ConfusedComposer is essential as a result of it exposes how behind-the-scenes interactions between cloud companies could be exploited via privilege escalation,” Matan defined. “On this case, an attacker solely wants permission to replace a Cloud Composer atmosphere to realize entry to essential GCP companies like Cloud Storage and Artifact Registry.”
Profitable exploitation of the flaw may allow an attacker to siphon delicate information, disrupt companies, and deploy malicious code inside CI/CD pipelines. Moreover, it may pave the best way for the deployment of backdoors that may grant persistent entry to compromised cloud environments.
Following accountable disclosure by Tenable, Google has addressed the vulnerability as of April 13, 2025, by eliminating the usage of the Cloud Construct service account to put in PyPI packages.
“The atmosphere’s service account might be used as a substitute,” Google stated in an announcement on January 15, 2025. “Current Cloud Composer 2 environments that beforehand used the default Cloud Construct service account will change to utilizing the atmosphere’s service account as a substitute.”
“Cloud Composer 2 environments created in variations 2.10.2 and later have already got this transformation. Cloud Composer 3 environments already use the atmosphere’s service account, and aren’t impacted by this transformation.”
The disclosure comes as Varonis Risk Labs uncovered a vulnerability in Microsoft Azure that would have allowed a risk actor with privileged entry to an Azure SQL Server to change configurations in a way that causes information loss upon admin motion. Microsoft has absolutely remediated the difficulty as of April 9, 2025, after it was made conscious of it on August 5, 2024.
The Harmful Saved URL Parameter Injection vulnerability, the corporate stated, stems from an absence of character limitation for server firewall guidelines created utilizing Transact-SQL (T-SQL).
“By manipulating the identify of server-level firewall guidelines via T-SQL, a risk actor with privileged entry to an Azure SQL Server can inject an implant that, based mostly on particular person actions, deletes arbitrary Azure sources that the person has permissions for,” safety researcher Coby Abrams stated.
“The impression of a risk actor exploiting this vulnerability could possibly be large-scale information loss within the affected Azure account.”
It additionally comes as Datadog Safety Labs make clear a bug in Microsoft Entra ID restricted administrative models that would allow an attacker to stop chosen customers from being modified, deleted, or disabled, even by a World Administrator.
“A privileged attacker may have used this bug to guard an account beneath their management, stopping containment by any Entra ID administrator,” safety researcher Katie Knowles stated. This included varied duties equivalent to resetting passwords, revoking person classes, deleting customers, and clearing person multi-factor authentication (MFA) strategies.
The difficulty has since been fastened by the Home windows maker as of February 22, 2025, following accountable disclosure on August 19, 2024.
In current weeks, risk actors have been discovered coaching their sights on web sites hosted on Amazon Internet Providers (AWS) Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) cases by exploiting Server-Aspect Request Forgery (SSRF) vulnerabilities to extract metadata data.
“EC2 Occasion Metadata is a function offered by AWS that enables an EC2 occasion to entry data wanted at runtime with no need to authenticate or make exterior API calls,” F5 Labs researcher Merlyn Albery-Speyer stated. “It could actually expose data equivalent to the general public or personal IP tackle, occasion ID, and IAM function credentials. A lot of that is delicate information of curiosity to attackers.”